Since the Java support for OSX has moved from Apple to Oracle. The old Java version are no longer shown in the oracle control panel:
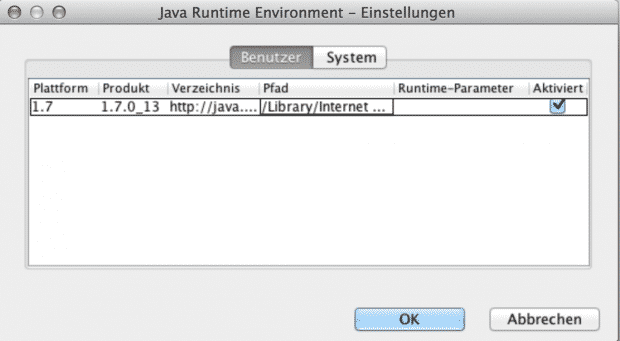
But there is a command line tool for selecting the java version:
$ /usr/libexec/java_home -h
Usage: java_home [options...]
Returns the path to a Java home directory from the current user's settings.
Options:
[-v/--version ] Filter Java versions in the "JVMVersion" form 1.X(+ or *).
[-a/--arch ] Filter JVMs matching architecture (i386, x86_64, etc).
[-d/--datamodel ] Filter JVMs capable of -d32 or -d64
[-t/--task ] Use the JVM list for a specific task (Applets, WebStart, BundledApp, JNI, or CommandLine)
[-F/--failfast] Fail when filters return no JVMs, do not continue with default.
[ --exec ...] Execute the $JAVA_HOME/bin/ with the remaining arguments.
[-R/--request] Request installation of a Java Runtime if not installed.
[-X/--xml] Print full JVM list and additional data as XML plist.
[-V/--verbose] Print full JVM list with architectures.
[-h/--help] This usage information.
You can check if you have a specific java version installed with this command:
/usr/libexec/java_home -v 1.6*
If 1.6 isn’t installed on your machine you can get it from here.
To use Java 1.6 in command line context add this line to your ~/.bash_profile:
export JAVA_HOME=`/usr/libexec/java_home -d64 -v 1.6*`

Information about Data protection